The C++ Standard Template Library (STL)
- Algorithms
- Containers
- Functions
- Iterators
Algorithms
The header algorithm defines a collection of functions especially designed to be used on ranges of elements.They act on containers and provide means for various operations for the contents of the containers.
- Algorithm
- Numeric
Containers
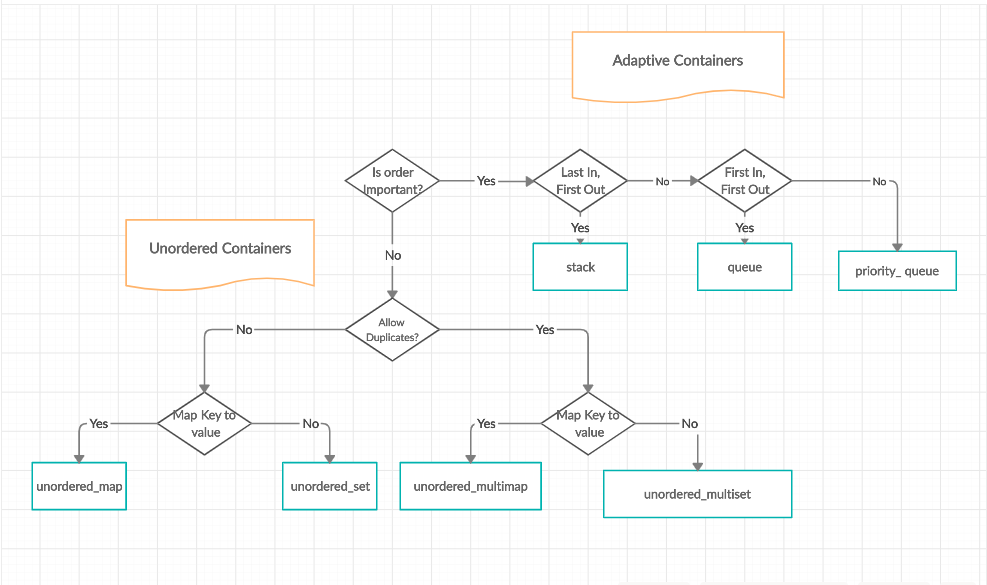
Containers or container classes store objects and data. There are in total seven standard “first-class” container classes and three container adaptor classes and only seven header files that provide access to these containers or container adaptors.
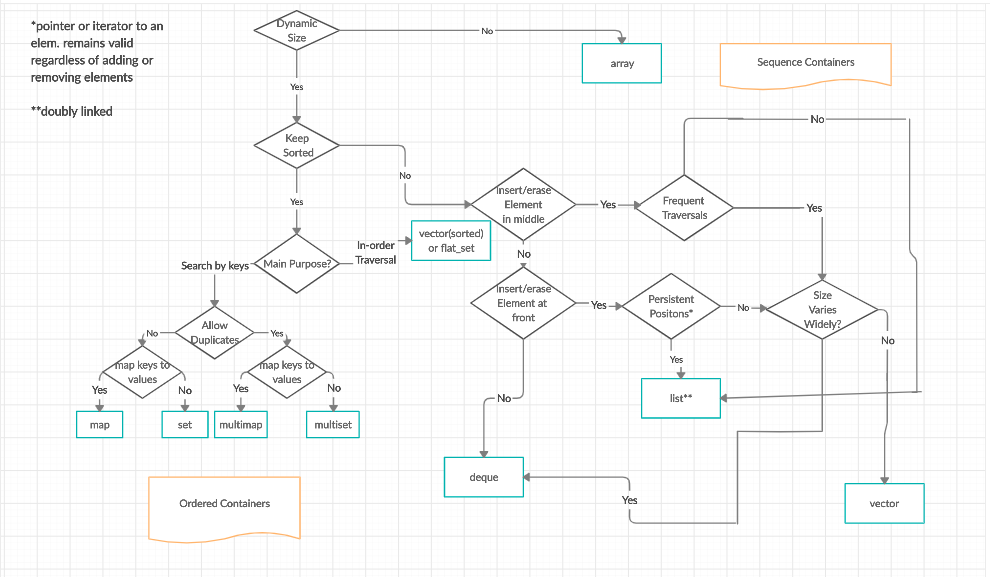
- Sequence Containers: implement data structures which can be accessed in a sequential manner.
- vector
- list
- deque
- arrays
- forward_list( Introduced in C++11)
- Container Adaptors : provide a different interface for sequential containers.
- Associative Containers : implement sorted data structures that can be quickly searched (O(log n) complexity).
- Unordered Associative Containers : implement unordered data structures that can be quickly searched
- unordered_set (Introduced in C++11)
- unordered_multiset (Introduced in C++11)
- unordered_map (Introduced in C++11)
- unordered_multimap (Introduced in C++11)
The Standard Template Library (STL) is a set of C++ template classes to provide common programming data structures and functions such as lists, stacks, arrays, etc. It is a library of container classes, algorithms, and iterators. It is a generalized library and so, its components are parameterized. A working knowledge of template classes is a prerequisite for working with STL.
STL has four components
- Algorithms
- Containers
- Functions
- Iterators
Algorithms
The header algorithm defines a collection of functions especially designed to be used on ranges of elements.They act on containers and provide means for various operations for the contents of the containers.
- Algorithm
- Numeric
Containers
Containers or container classes store objects and data. There are in total seven standard “first-class” container classes and three container adaptor classes and only seven header files that provide access to these containers or container adaptors.
- Sequence Containers: implement data structures which can be accessed in a sequential manner.
- vector
- list
- deque
- arrays
- forward_list( Introduced in C++11)
- Container Adaptors : provide a different interface for sequential containers.
- Associative Containers : implement sorted data structures that can be quickly searched (O(log n) complexity).
- Unordered Associative Containers : implement unordered data structures that can be quickly searched
- unordered_set (Introduced in C++11)
- unordered_multiset (Introduced in C++11)
- unordered_map (Introduced in C++11)
- unordered_multimap (Introduced in C++11)
Functions
The STL includes classes that overload the function call operator. Instances of such classes are called function objects or functors. Functors allow the working of the associated function to be customized with the help of parameters to be passed.
Iterators
As the name suggests, iterators are used for working upon a sequence of values. They are the major feature that allow generality in STL.
Hope you have already understood the concept of C++ Template which we have discussed earlier. The C++ STL (Standard Template Library) is a powerful set of C++ template classes to provide general-purpose classes and functions with templates that implement many popular and commonly used algorithms and data structures like vectors, lists, queues, and stacks.
At the core of the C++ Standard Template Library are following three well-structured components −
| Sr.No | Component & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Containers
Containers are used to manage collections of objects of a certain kind. There are several different types of containers like deque, list, vector, map etc.
|
| 2 |
Algorithms
Algorithms act on containers. They provide the means by which you will perform initialization, sorting, searching, and transforming of the contents of containers.
|
| 3 |
Iterators
Iterators are used to step through the elements of collections of objects. These collections may be containers or subsets of containers.
|
We will discuss about all the three C++ STL components in next chapter while discussing C++ Standard Library. For now, keep in mind that all the three components have a rich set of pre-defined functions which help us in doing complicated tasks in very easy fashion.
Let us take the following program that demonstrates the vector container (a C++ Standard Template) which is similar to an array with an exception that it automatically handles its own storage requirements in case it grows −
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; int main() { // create a vector to store int vector<int> vec; int i; // display the original size of vec cout << "vector size = " << vec.size() << endl; // push 5 values into the vector for(i = 0; i < 5; i++) { vec.push_back(i); } // display extended size of vec cout << "extended vector size = " << vec.size() << endl; // access 5 values from the vector for(i = 0; i < 5; i++) { cout << "value of vec [" << i << "] = " << vec[i] << endl; } // use iterator to access the values vector<int>::iterator v = vec.begin(); while( v != vec.end()) { cout << "value of v = " << *v << endl; v++; } return 0; }
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
vector size = 0 extended vector size = 5 value of vec [0] = 0 value of vec [1] = 1 value of vec [2] = 2 value of vec [3] = 3 value of vec [4] = 4 value of v = 0 value of v = 1 value of v = 2 value of v = 3 value of v = 4
Here are following points to be noted related to various functions we used in the above example −
- The push_back( ) member function inserts value at the end of the vector, expanding its size as needed.
- The size( ) function displays the size of the vector.
- The function begin( ) returns an iterator to the start of the vector.
- The function end( ) returns an iterator to the end of the vector.
The C++ Standard Library can be categorized into two parts −
- The Standard Function Library − This library consists of general-purpose,stand-alone functions that are not part of any class. The function library is inherited from C.
- The Object Oriented Class Library − This is a collection of classes and associated functions.
Standard C++ Library incorporates all the Standard C libraries also, with small additions and changes to support type safety.
The Standard Function Library
The standard function library is divided into the following categories −
- I/O,
- String and character handling,
- Mathematical,
- Time, date, and localization,
- Dynamic allocation,
- Miscellaneous,
- Wide-character functions,
The Object Oriented Class Library
Standard C++ Object Oriented Library defines an extensive set of classes that provide support for a number of common activities, including I/O, strings, and numeric processing. This library includes the following −
- The Standard C++ I/O Classes
- The String Class
- The Numeric Classes
- The STL Container Classes
- The STL Algorithms
- The STL Function Objects
- The STL Iterators
- The STL Allocators
- The Localization library
- Exception Handling Classes
- Miscellaneous Support Library
3 Comments
Nice work man
ReplyDeleteNice explanation
ReplyDeletebahut hi sundar
ReplyDelete