Templates are the foundation of generic programming, which involves writing code in a way that is independent of any particular type.

A template is a blueprint or formula for creating a generic class or a function. The library containers like iterators and algorithms are examples of generic programming and have been developed using template concept.
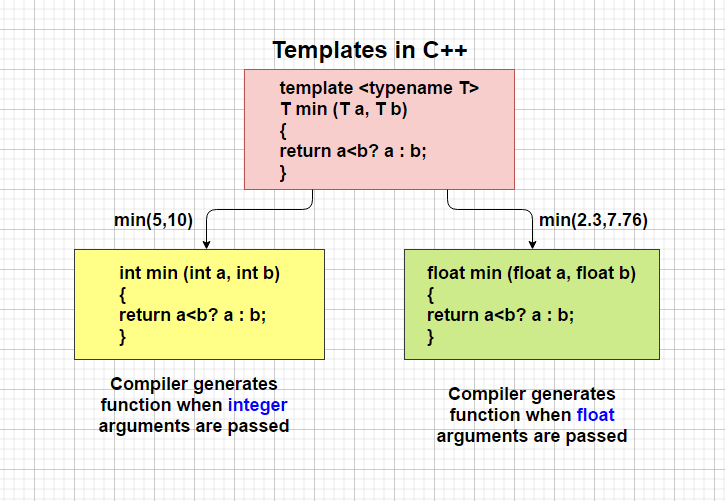

There is a single definition of each container, such as vector, but we can define many different kinds of vectors for example, vector <int> or vector <string>.
You can use templates to define functions as well as classes, let us see how they work −
Function Template
The general form of a template function definition is shown here −
template <class type> ret-type func-name(parameter list) {
// body of function
}
Here, type is a placeholder name for a data type used by the function. This name can be used within the function definition.
The following is the example of a function template that returns the maximum of two values −
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; template <typename T> inline T const& Max (T const& a, T const& b) { return a < b ? b:a; } int main () { int i = 39; int j = 20; cout << "Max(i, j): " << Max(i, j) << endl; double f1 = 13.5; double f2 = 20.7; cout << "Max(f1, f2): " << Max(f1, f2) << endl; string s1 = "Hello"; string s2 = "World"; cout << "Max(s1, s2): " << Max(s1, s2) << endl; return 0; }
If we compile and run above code, this would produce the following result −
Max(i, j): 39 Max(f1, f2): 20.7 Max(s1, s2): World
Class Template
Just as we can define function templates, we can also define class templates. The general form of a generic class declaration is shown here −
template <class type> class class-name {
.
.
.
}
Here, type is the placeholder type name, which will be specified when a class is instantiated. You can define more than one generic data type by using a comma-separated list.
Following is the example to define class Stack<> and implement generic methods to push and pop the elements from the stack −
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> #include <string> #include <stdexcept> using namespace std; template <class T> class Stack { private: vector<T> elems; // elements public: void push(T const&); // push element void pop(); // pop element T top() const; // return top element bool empty() const { // return true if empty. return elems.empty(); } }; template <class T> void Stack<T>::push (T const& elem) { // append copy of passed element elems.push_back(elem); } template <class T> void Stack<T>::pop () { if (elems.empty()) { throw out_of_range("Stack<>::pop(): empty stack"); } // remove last element elems.pop_back(); } template <class T> T Stack<T>::top () const { if (elems.empty()) { throw out_of_range("Stack<>::top(): empty stack"); } // return copy of last element return elems.back(); } int main() { try { Stack<int> intStack; // stack of ints Stack<string> stringStack; // stack of strings // manipulate int stack intStack.push(7); cout << intStack.top() <<endl; // manipulate string stack stringStack.push("hello"); cout << stringStack.top() << std::endl; stringStack.pop(); stringStack.pop(); } catch (exception const& ex) { cerr << "Exception: " << ex.what() <<endl; return -1; } }
If we compile and run above code, this would produce the following result −
7 hello Exception: Stack<>::pop(): empty stack
0 Comments